


Indicates the device will be on in a zero gate-source voltage state.
#FET TRANSISTOR CHARACTERISTICS HOW TO#
For more information on current sensing please visit How to Select and Apply Smart Current Sensing and Monitoring Technologies A current-sensing MOSFET uses a small portion of these parallel cells to form a second low-power MOSFET (also called a senseFET) that is isolated from the power device, having a common gate and drain but a separate source that is brought out as a SENSE pin. Modern power MOSFETs comprise thousands of identical transistor cells connected in parallel to minimize the overall on-resistance (RDS(ON)). Input Capacitance (Ciss) (Max) Vds: Characterizes the sum of a device’s parasitic gate-to-drain and gate-to-source capacitances, measured at the indicated value of drain-source voltage.įET Feature: Indicates distinguishing aspects of device construction or operating characteristics.
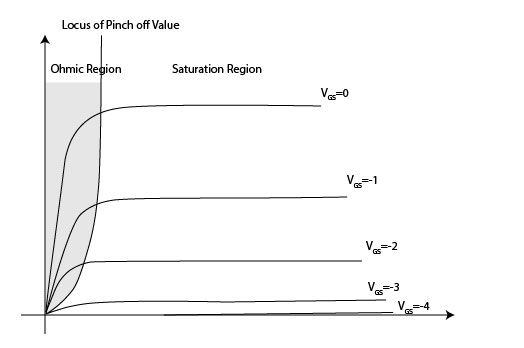
Vgs (Max): The maximum voltage that may be applied across the gate and source terminals of a device without causing damage. Gate Charge (Qg) (Max) Vgs: Characterizes the amount of electrical charge required to change an applied gate-source voltage from zero to the value shown, under manufacturer-defined test conditions. Vgs(th) (Max) Id: Characterizes the magnitude of the gate-source voltage at which a device turns “on” sufficiently to allow a drain current of the indicated magnitude to flow. See datasheets for applicable thermal test conditions. Rds On (Max) Id, Vgs: The manufacturer’s specified maximum on-state drain-source resistance measured under the indicated test conditions. Allowable values in practice are subject to thermal limitations and may be much less than those indicated.ĭrive Voltage (MAX rds On, Min Rds On): Indicates the gate-source voltage(s) at which the device’s on-state resistance is numerically characterized by the manufacturer. Magnitude of manufacturer’s ratings shown.Ĭurrent - Continuous Drain (ID) 25☌: Manufacturer’s indicated maximum drain current(s), subject to maintenance of a case (Tc) or ambient (Ta) temperature of 25☌. Technology: Typically Identifies the material composition of the device.ĭrain to Source Voltage: The absolute maximum voltage between drain and source terminals that a device is rated to withstand. Specifications to determine which FET/MOSFET is right for your application.įET Type: FET channel type influences the polarity of voltages applied to the device in typical use. They are used almost universally for applications requiring voltage ratings of a few hundred volts or less, above which other device types such as IGBTs become more competitive. Single FETs, MOSFETs - Discrete Field Effect Transistors (FETs), and Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) are widely used in power conversion, motor control, solid-state lighting, and other applications where their characteristic ability to be switched on & off at high frequencies while carrying substantial amounts of current is advantageous. This Product Selection Guide contains information to help select products in the Discrete Semiconductor - Transistors - Single FETs, MOSFETs category on


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
